- Laboratory Guide: Determination of Caffeine Content in Roasted Coffee
Scope and Principle
Scope: This procedure applies to roasted coffee beans and roasted ground coffee. It determines the caffeine content expressed on a dry-matter basis (i.e. corrected for sample moisture content). The method is intended as a reference procedure for caffeine analysis in coffee.
Principle: Caffeine (C₈H₁₀N₄O₂) is liberated from the coffee matrix by boiling the sample in water with magnesium oxide (MgO). Magnesium oxide creates basic conditions that free caffeine from bound forms or acidic interferents. The caffeine is then extracted into chloroform by liquid–liquid extraction. The purified extract is subjected to a Kjeldahl nitrogen determination. Because caffeine contains a known proportion of nitrogen (four atoms per molecule), the nitrogen measured is converted to caffeine content using a factor, reported as % caffeine by dry mass.
Health and Safety Precautions
EXTREME CAUTION: This method involves hazardous chemicals and procedures (boiling solvents, strong acids/bases, and toxic reagents). All steps must be performed in a certified fume hood with safety controls.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Lab coat, goggles, nitrile/neoprene gloves, closed shoes, long pants.
Chemical Hazards:
- Chloroform (CHCl₃): Volatile, toxic by inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Possibly carcinogenic (IARC 2B). Use only in fume hood.
- Concentrated Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Highly corrosive. Causes burns and blindness. Always add acid to water, not water to acid.
- Concentrated Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Extremely corrosive. Causes deep burns. Heat released when mixing with water.
- Mercuric Oxide (HgO): Highly toxic heavy-metal catalyst. Avoid inhalation or skin contact. Mercury is cumulative and harmful.
Waste Disposal: Collect all waste as hazardous chemical waste. Separate chloroform, acid/base solutions, and mercury residues in clearly labeled containers. Never dispose of mercury in drains or trash.
General Safety: Know emergency shower/eyewash. Keep spill kit. Only trained personnel may perform this analysis. Never leave unattended during heating or distillation.
Apparatus and Equipment
- Analytical balance: ±0.1 mg accuracy.
- 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks with reflux condenser.
- Heating mantle or hot plate: for boiling under reflux.
- 50 mL volumetric flask: for aliquot collection.
- 125 mL separatory funnels: for chloroform extraction and KOH wash.
- Filter paper: medium or fast flow.
- Cotton plugs: to retain aqueous droplets.
- 100 mL Kjeldahl flask: for digestion and distillation.
- Kjeldahl digestion unit: for sulfuric acid digestion.
- Kjeldahl distillation apparatus: for ammonia distillation into standard acid.
- Receiving flask: with standard acid and indicator.
- Burette (50 mL): for titration with NaOH.
- Water bath (optional): for chloroform evaporation.
Reagents and Materials
All reagents must be analytical grade. Water must be distilled/deionized (ISO 3696).
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO): High-grade ignited powder.
- Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Dilute 1:9 for extraction, concentrated for digestion.
- Chloroform (CHCl₃): Redistilled, pure. Toxic.
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) 1%: For washing chloroform extract.
- Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄): Digestion accelerator.
- Mercuric Oxide (HgO): Catalyst for digestion. Highly toxic.
- Sodium Hydroxide (~50%): For distillation step.
- Standard Sulfuric Acid 0.05 N: Receiver solution.
- Standard Sodium Hydroxide ~0.1 N: Titrant, standardized.
- Methyl Red Indicator: For titration endpoint.
Moisture determination: Required to express results on dry basis.
Detailed Procedure
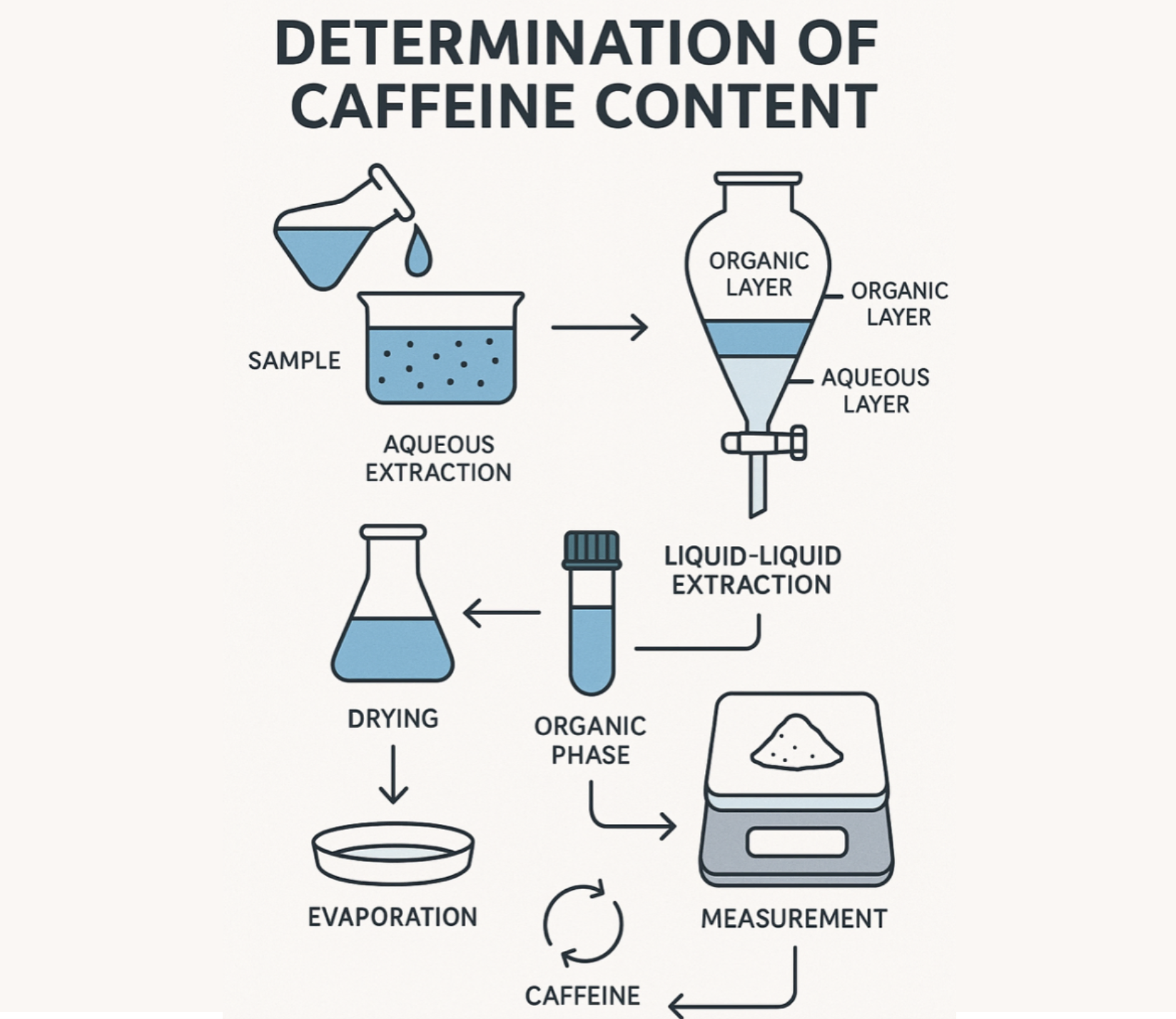
Workflow: (1) Sample Preparation → (2) Aqueous Extraction → (3) Solvent Extraction → (4) Purification → (5) Kjeldahl Digestion → (6) Distillation → (7) Titration → (8) Calculation.
Sample Preparation
- Grind or homogenize sample to prescribed fineness.
- Weigh ~5.0 g into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Record mass.
- Note moisture content (or analyze separately).
Extraction and Purification
- Add 3.0 g MgO and 100 mL water to flask.
- Attach reflux condenser and boil for 45 min.
- Cool, restore lost mass with water, mix.
- Filter and collect 50 mL extract into volumetric flask (represents ½ sample).
- Transfer to separatory funnel, add 4 mL dilute H₂SO₄.
- Extract with chloroform 5 × 10 mL. Combine chloroform layers.
- Wash chloroform with 5 mL 1% KOH. Drain chloroform through cotton into Kjeldahl flask.
- Rinse with 5 mL chloroform, add to flask. Remove cotton.
Digestion (Kjeldahl)
- Add 1.3 g K₂SO₄ and 40 mg HgO.
- Evaporate chloroform gently.
- Add 2.0 mL concentrated H₂SO₄ carefully.
- Digest until solution clears (~1 h). Do not dry-boil.
- Cool and dilute with 5 mL water.
Distillation and Titration
- Setup Kjeldahl apparatus. Receiver: 25 mL 0.05 N H₂SO₄ with methyl red.
- Add ~6 mL concentrated NaOH to digest (carefully). Mix and connect apparatus.
- Distill ammonia into receiver until ≥150 mL distillate collected.
- Titrate excess acid with 0.1 N NaOH to yellow endpoint.
- Run blank with same reagents for correction.
Calculation
Caffeine (% dry basis):
Caffeine = (484.96 × (B - A) × M) / [m × (100 - m_c)]
- B = blank NaOH volume (mL)
- A = sample NaOH volume (mL)
- M = molarity of NaOH titrant
- m = mass of sample represented in aliquot (g)
- m_c = moisture content (%)
Quality Control
- Run reagent blank for correction.
- Perform duplicate analysis (RPD < 10%).
- Check spike recovery (90–110%).
- Analyze CRM if available.
- Maintain instrument calibration.
Notes and Limitations
- Specificity: Measures nitrogen as proxy for caffeine.
- Labor: Method is lengthy and hazardous; HPLC is faster and safer.
- Hazards: Consider mercury-free catalysts or alternative solvents.
- Moisture: Report results on dry basis; correct using % moisture.
- Expected ranges: Arabica 1.0–1.5%, Robusta 2.0–2.5% caffeine.
- Documentation: Record all weights, volumes, burette readings, and calculations.
By following this guide carefully, you will obtain a reliable measurement of caffeine in roasted coffee by the Kjeldahl reference method.
- For more information:
? : Contact Us